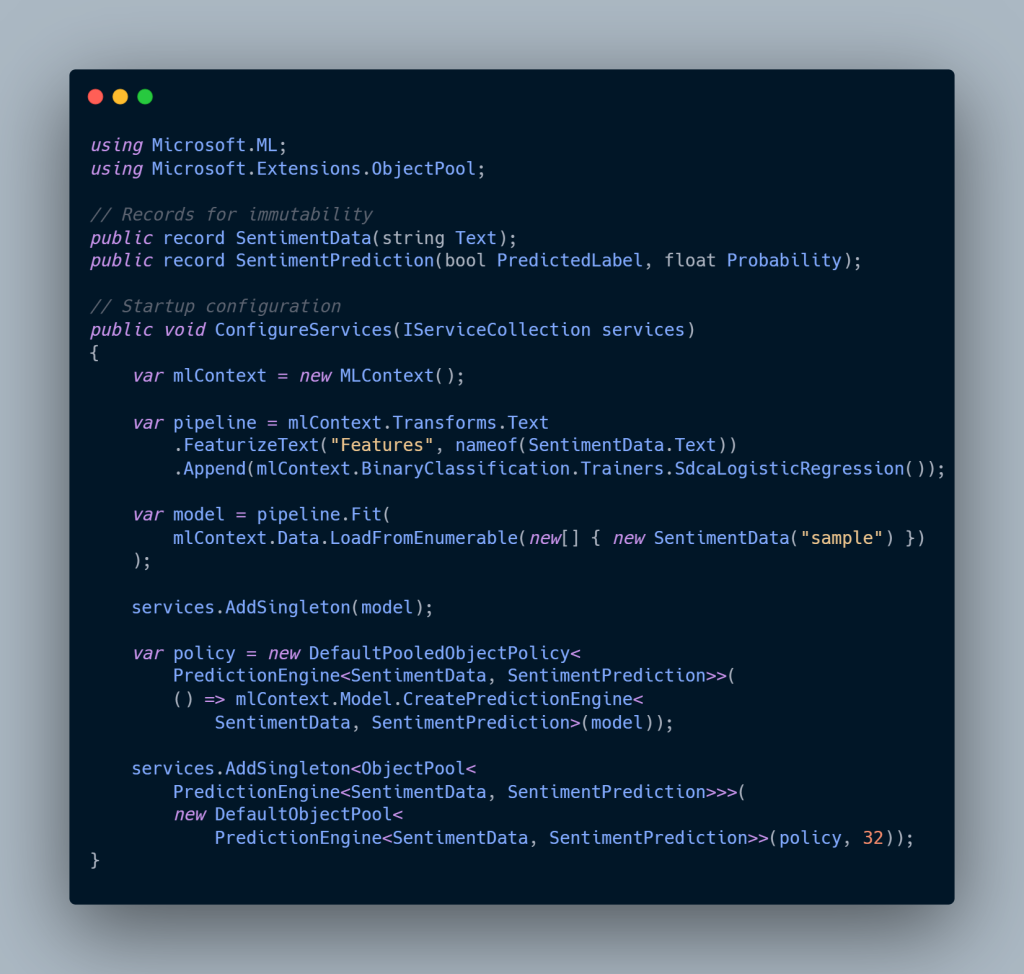
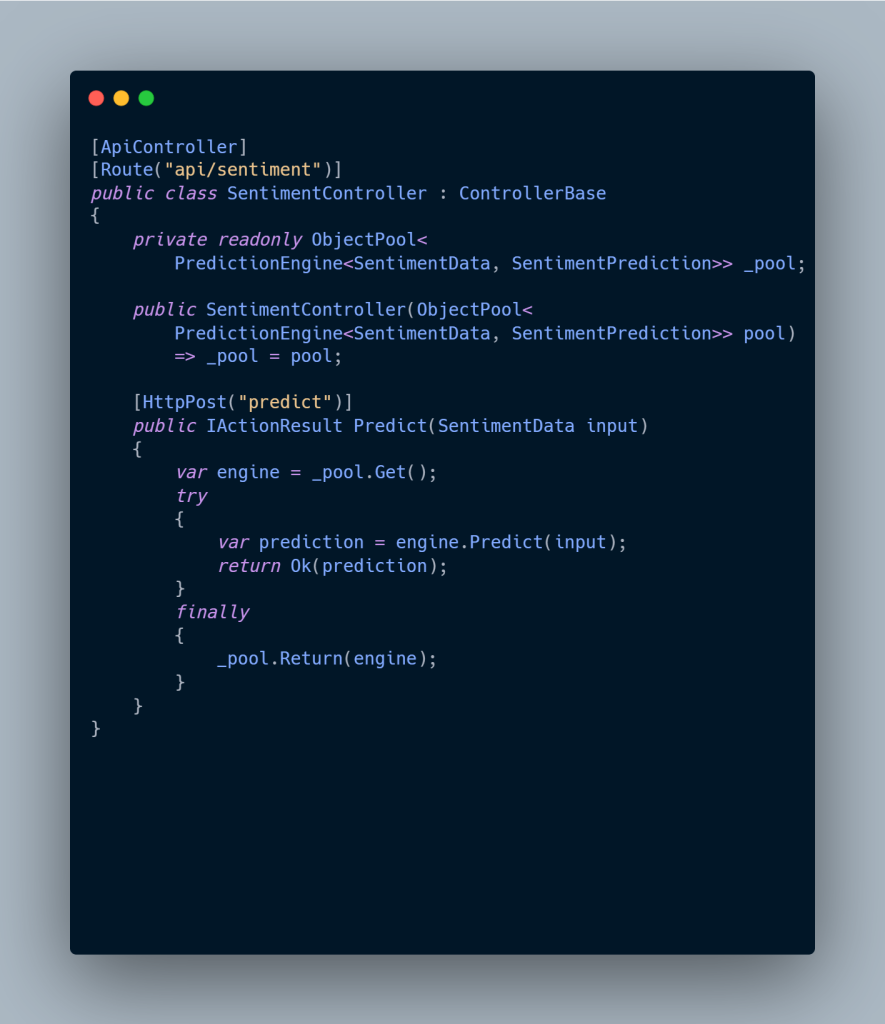
Modern .NET development keeps pushing toward simplicity, clarity, and performance. With C# 12+, developers can eliminate noisy constructors, streamline collection handling, and write APIs that feel effortless to maintain. Developers building modern .NET applications with C# 12 gain immediate benefits from clearer syntax and reduced boilerplate.
By adopting features like primary constructors, collection expressions, params collections, and inline arrays, teams routinely cut 30–40% of ceremony out of codebases while keeping enterprise scalability intact.
Why Build Modern .NET Applications with C# 12?
Modern .NET applications with C# 12 allow teams to write cleaner, more efficient code without the structural noise that older C# versions required.
Prerequisites for Building Modern .NET Applications with C# 12
Tools Required
- Visual Studio 2022 or VS Code + C# Dev Kit
- .NET 8 SDK (C# 12)
- .NET 10 SDK (future-ready)
Recommended NuGet Packages
dotnet add package Microsoft.AspNetCore.OpenApi
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
Knowledge Required
- Dependency injection
- ASP.NET Core
- LINQ and lambdas
- EF Core basics
Primary Constructors: Transforming Modern .NET Applications with C# 12
Old DI Pattern (Verbose)
public class UserService
{
private readonly IUserRepository _userRepository;
private readonly ILogger<UserService> _logger;
private readonly IEmailService _emailService;
public UserService(
IUserRepository userRepository,
ILogger<UserService> logger,
IEmailService emailService)
{
_userRepository = userRepository;
_logger = logger;
_emailService = emailService;
}
public async Task CreateUserAsync(string email)
{
_logger.LogInformation($"Creating user: {email}");
await _userRepository.AddAsync(new User { Email = email });
await _emailService.SendWelcomeEmailAsync(email);
}
}
Modern Primary Constructor (Clean C# 12)
public class UserService(
IUserRepository userRepository,
ILogger<UserService> logger,
IEmailService emailService)
{
public async Task<User> CreateUserAsync(string email)
{
logger.LogInformation($"Creating user: {email}");
var user = new User { Email = email };
await userRepository.AddAsync(user);
await emailService.SendWelcomeEmailAsync(email);
return user;
}
public Task<User?> GetUserAsync(int id) =>
userRepository.GetByIdAsync(id);
}
Real Business Logic Example
public class OrderProcessor(
IOrderRepository orderRepository,
IPaymentService paymentService,
ILogger<OrderProcessor> logger)
{
private const decimal MinimumOrderAmount = 10m;
public async Task<OrderResult> ProcessOrderAsync(Order order)
{
if (order.TotalAmount < MinimumOrderAmount)
{
logger.LogWarning(
$"Order amount {order.TotalAmount} below minimum");
return OrderResult.Failure("Order amount too low");
}
try
{
var payment = await paymentService.ChargeAsync(order.TotalAmount);
if (!payment.IsSuccessful)
{
logger.LogError($"Payment failed: {payment.ErrorMessage}");
return OrderResult.Failure(payment.ErrorMessage);
}
order.Status = OrderStatus.Paid;
await orderRepository.UpdateAsync(order);
logger.LogInformation($"Order {order.Id} processed successfully");
return OrderResult.Success(order);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
logger.LogError(ex, "Unexpected error processing order");
return OrderResult.Failure("Unexpected error occurred");
}
}
}
Collection Expressions in Modern .NET Applications with C# 12
Old Collection Syntax
int[] numbers = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
List<string> names = new List<string> { "Alice", "Bob", "Charlie" };
int[][] jagged = new int[][]
{
new int[] { 1, 2 },
new int[] { 3, 4 }
};
Modern C# 12 Syntax
int[] numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
List<string> names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"];
int[][] jagged = [[1, 2], [3, 4]];
Spread Syntax
int[] row0 = [1, 2, 3];
int[] row1 = [4, 5, 6];
int[] row2 = [7, 8, 9];
int[] combined = [..row0, ..row1, ..row2];
Real API Example
public class ProductService(IProductRepository repository)
{
public async Task<ProductListResponse> GetFeaturedProductsAsync()
{
var products = await repository.GetFeaturedAsync();
return new ProductListResponse
{
Products =
[
..products.Select(p => new ProductDto(
p.Id, p.Name, p.Price, [..p.Tags]))
],
TotalCount = products.Count,
Categories = ["Electronics", "Clothing", "Books"]
};
}
}
public record ProductDto(int Id, string Name, decimal Price, List<string> Tags);
public record ProductListResponse
{
public required List<ProductDto> Products { get; init; }
public required int TotalCount { get; init; }
public required List<string> Categories { get; init; }
}
Minimal APIs in Modern .NET Applications with C# 12
Old Minimal API
app.MapPost("/users",
async (CreateUserRequest request, UserService service) =>
{
var user = await service.CreateUserAsync(request.Email);
return Results.Created($"/users/{user.Id}", user);
});
Modern Minimal API With Metadata
app.MapPost("/users", async (
[FromBody] CreateUserRequest request,
[FromServices] UserService service,
[FromServices] ILogger<UserService> logger) =>
{
logger.LogInformation($"Creating user: {request.Email}");
var user = await service.CreateUserAsync(request.Email);
return Results.Created($"/users/{user.Id}", user);
})
.WithName("CreateUser")
.WithOpenApi()
.Produces(StatusCodes.Status201Created)
.Produces(StatusCodes.Status400BadRequest);
Inline Arrays (Performance Boost in Modern .NET Applications with C# 12)
[System.Runtime.CompilerServices.InlineArray(10)]
public struct IntBuffer
{
private int _element0;
}
public class DataProcessor
{
public void ProcessBatch(ReadOnlySpan<int> data)
{
var buffer = new IntBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < data.Length && i < 10; i++)
buffer[i] = data[i];
foreach (var item in buffer)
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
Final Thoughts on Modern .NET Applications with C# 12
With C# 12+, enterprise .NET apps benefit from:
✔ Less boilerplate
✔ Cleaner collections
✔ Metadata-rich lambdas
✔ Higher performance
By integrating these language features, teams building modern .NET applications with C# 12 unlock easier code maintenance, faster development, and fewer bugs.
You might be interested in
AI-Native .NET: Building Intelligent Applications with Azure OpenAI, Semantic Kernel, and ML.NET
Master Effortless Cloud-Native .NET Microservices Using DAPR, gRPC & Azure Kubernetes Service
🟣 Microsoft Official Docs
➡ C# 12 Language Features
https://learn.microsoft.com/dotnet/csharp/whats-new/csharp-12
➡ Minimal APIs (.NET 8)
https://learn.microsoft.com/aspnet/core/fundamentals/minimal-apis
➡ Primary Constructors Proposal
https://learn.microsoft.com/dotnet/csharp/language-reference/proposals/csharp-12.0/primary-constructors